Special Report
The AI Handbook
- Introduction
- Are AI Concerns Overblown? Here’s Why History Says It’s Time to Put AI in Your Portfolio TODAY
- Beyond ChatGPT: Understanding How Businesses – and Individuals – Are Harnessing AI Right Now (And Where We’re Heading)
- Diagnosis: Profits! The Sector Most Ripe for AI Innovation
- How to Start Using AI Now… and Gain Some Valuable Know-How in the Process
- In Sum: AI Terminology and FAQs
Introduction
It feels as though many, many moons have passed since OpenAI introduced ChatGPT to the world.
But as of this writing… it’s been less than three years.
Still, three years is a long time in the tech world. And it’s practically eons in the age of smart devices.
It was long enough for the cultural conversation to shift from “Is artificial intelligence safe? Is it ethical?”
To…
“If you aren’t using AI, you’re falling behind.”
That’s an excerpt from a Forbes headline, by the way.
All of a sudden, it seems that if you’re not betting big on AI… your company is going to be left in the digital dust.
And if you’re not investing in AI? Well, then you’ve already missed out on some tremendous gains.
Take Nvidia’s (NVDA) 200% rise in 2023. Or Microsoft’s (MSFT) 64% run-up after it announced it would invest $10 billion in OpenAI.
The promise of AI even revived Alphabet (GOOGL) shares, which had plummeted 38% during 2022.
After the company announced and then launched Bard, its ChatGPT competitor, in 2023, the stock jumped 34%.
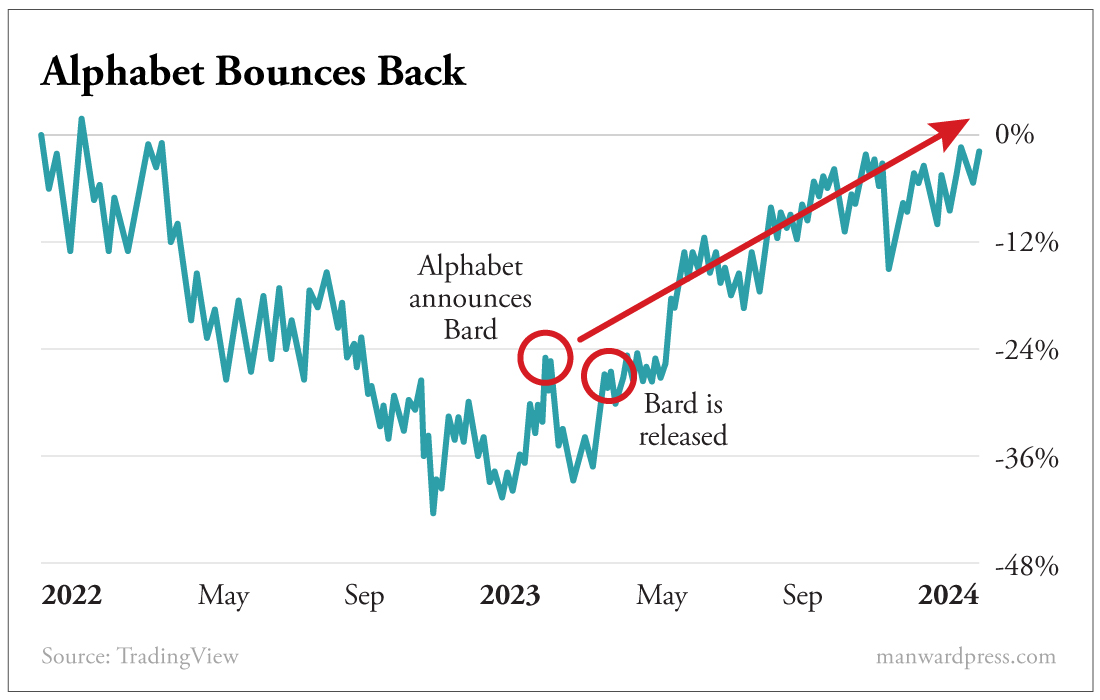
Today it’s up 55% from the day it announced Bard (now rebranded as Gemini).
It’s no exaggeration to say that AI has propped up the markets in recent years. And that’s a trend that shows no sign of slowing.
“Analysts bullish on the market acknowledge the concentration at the top but expect the AI-driven gains to broaden as the technology pervades the economy and smaller companies gain notoriety.” – ABC News
It probably goes without saying that AI has been good news for Manward portfolios.
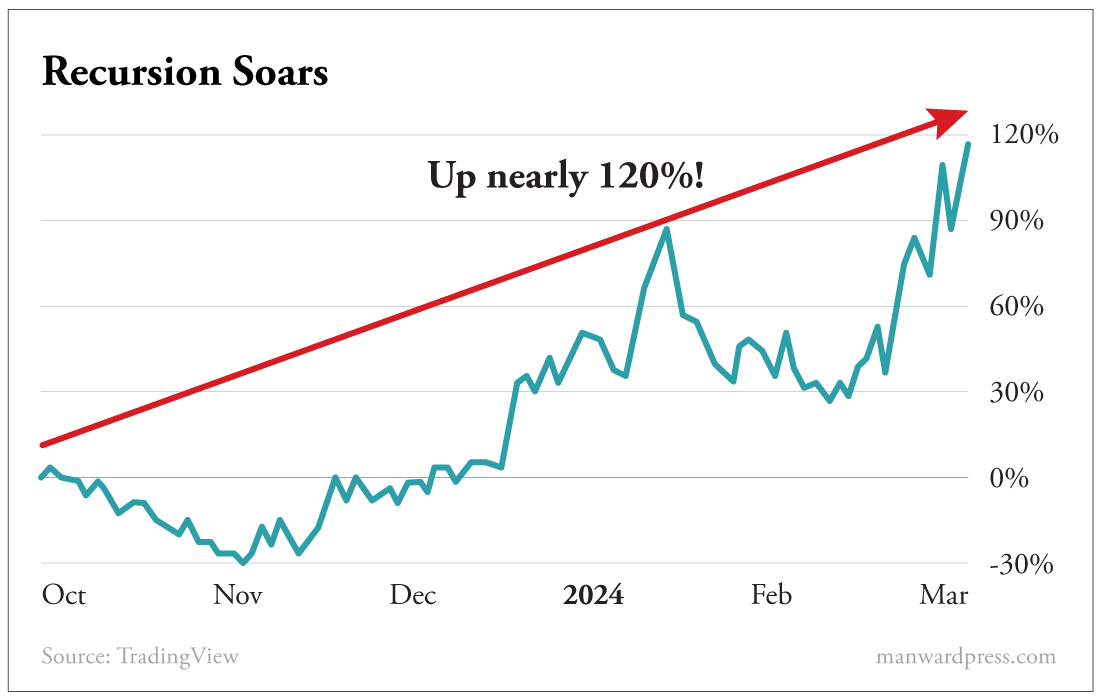
Recursion Pharmaceuticals (RXRX) soared shortly after we recommended it in the October 2023 issue of Manward Money Report.
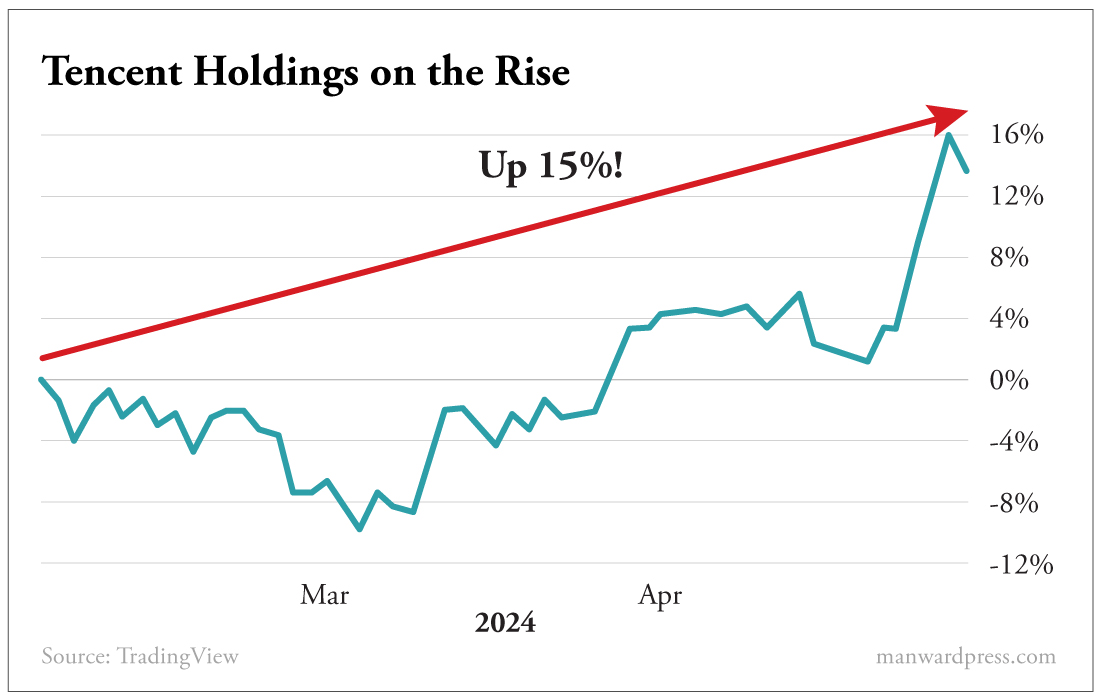
And Tencent Holdings (TCEHY), recommended in our February 2024 issue of Manward Money Report, has jumped 15% in the time since we added it to the Base Builders section of our Modern Asset Portfolio.
Both stocks are proof that the AI boom is backed by something far more solid than the chatbots and bizarre works of “art” that have permeated the internet since ChatGPT’s launch.
Despite what some still seem to think… there is real utility here.
World-changing utility.
Analysts estimate that businesses already using AI are boosting their productivity by between 21% and 36%. And a Forbes Advisor survey found that 73% of businesses plan to use AI to beef up their customer service operations. More than half of respondents said they’ve started using AI to automate their production processes.
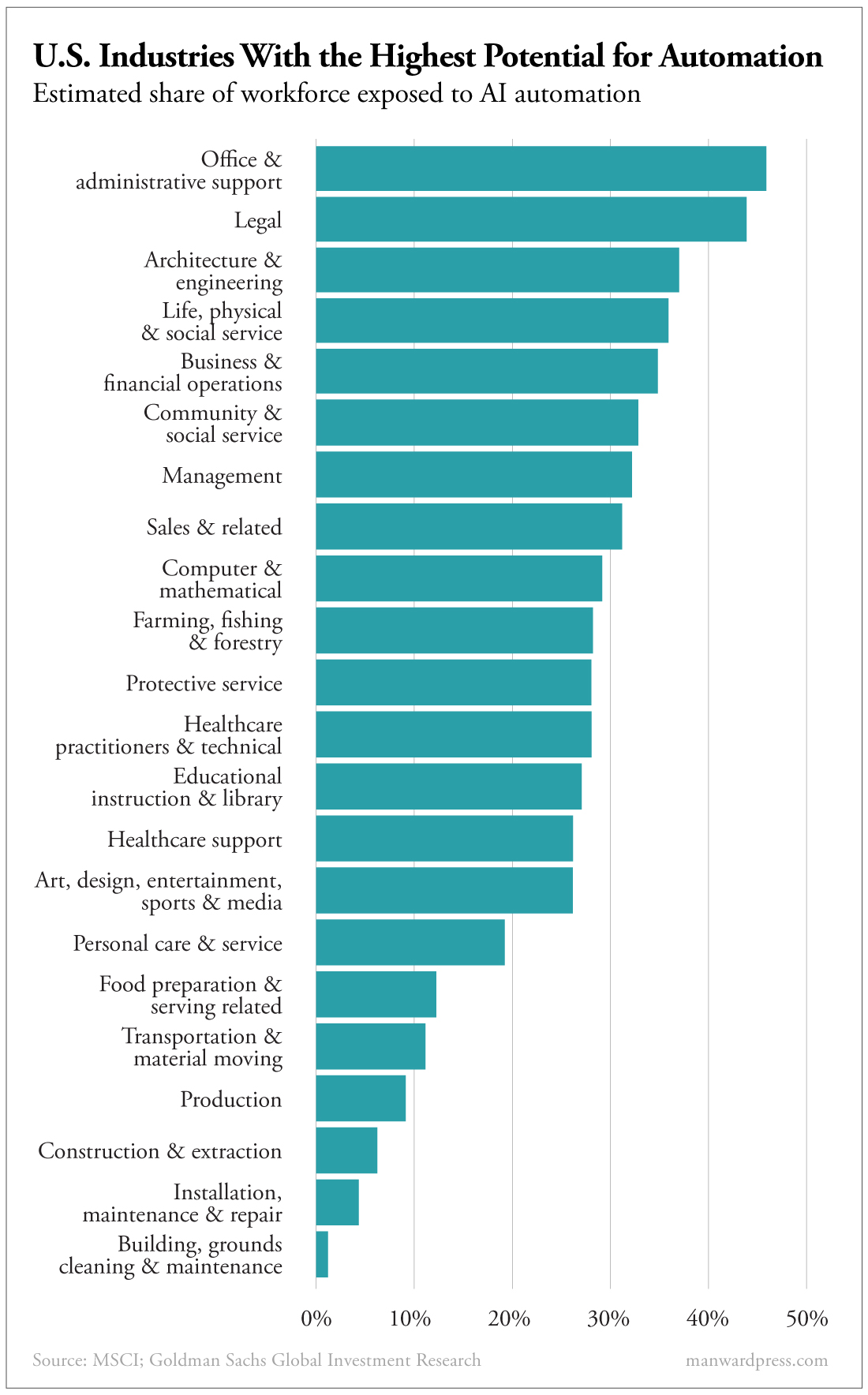
Looking ahead, experts believe AI holds the key to unlocking long-brewing technological advancements like autonomous cars… predictive healthcare that could greatly extend lives… and smart grid automation that could help put an end to blackouts and other disasters.
The impact will be sweeping.
And that’s precisely why we put together this easy-to-digest handbook.
Our goal is to quickly catch you up on what’s happened so far with AI… and prime you for all that is to come…
The best areas to invest…
The best way to get started using AI yourself…
How AI can help you analyze companies…
And more.
Let’s get started, first, by dispelling some major AI myths.
Are AI Concerns Overblown? Here’s Why History Says It’s Time to Put AI in Your Portfolio TODAY
Everybody is worried about the AI gold rush.
They say AI is going to ruin the world.
But, as usual, Manward is taking a different approach.
Get this: Writing-assistance software Grammarly now offers a plug-in for your email that will help ensure you don’t accidentally send a gruff message.
For just $12 a month, it’ll scan your messages as you write them and offer “softer” suggestions.
I imagine a line like “You’re an idiot” will turn into something like “I’m not sure I agree with your line of thinking.”
It may sound a bit underwhelming at first blush. But then again, who hasn’t had a colleague who would be in the C-suite by now if they’d had a tool like this lording over their emails… or, even better, their mouths.
Lots of folks are pondering what AI will do to the writing world. Will it put Manward out of business? Will our readers soon prefer the half-witted humor and off-center views of some silicon-based microprocessor?
With the market suddenly flooded by AI-generated pieces, folks in the art world are now paying a premium for work that carries the mark of a human being.
And you know what? We’re not worried.
Follow the Money
The rise of the automobile put plenty of farriers out of work. They no doubt put up a fight. But the world’s economy survived.
In fact… it got a whole lot better. Those farriers found other work.
If AI can make Manward’s output better (and keep us from saying offensive things), good on it.
Money, after all, goes where it’s treated best.
If AI can produce better writers, it can produce better cancer drugs. (More on that in an upcoming chapter.) It can produce better ways of reducing crime. It can produce safer cars. It can produce better materials… more efficient products… and, dare we say it, better economic forecasts.
The folks who say this technology will force half the nation onto some government-funded minimum-income program could use a bit more natural intelligence.
They’re forgetting the core human incentive that drives everything… greed.
If half the population gives up its thirst for more and sits on the couch crying about being defeated by robots… we’re in big trouble.
We’re convinced we’re at the dawn of something big… something even more revolutionary and economically influential than the internet.
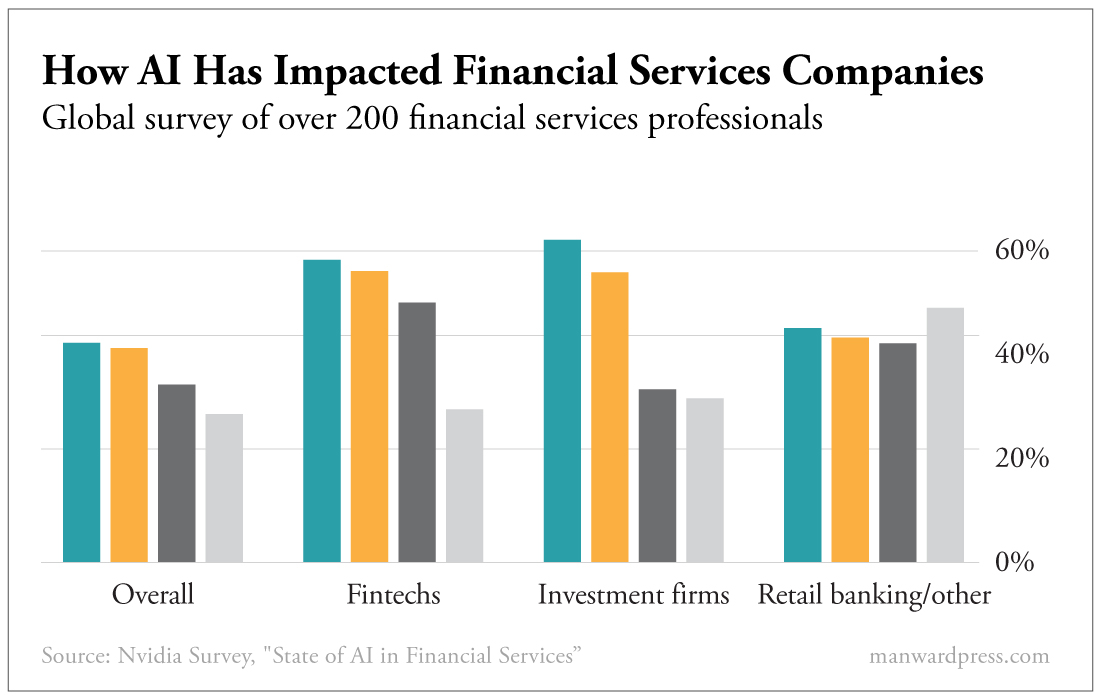
According to IBM, 77% of companies are either already using or exploring the use of AI.
Thirty-five percent of businesses say they are currently training their employees to use AI and automation tools.
And they’re investing in the tech necessary to take full advantage of AI over the months ahead.
That’s why we’re seeing stocks like Nvidia catch a bid – and soar by more than 200% – as investors rush in.
But at Manward we aren’t limited to finding the best AI stocks to invest in… or waiting for AI’s next big success story.
No. You can start using AI in your investing today.
Invest With the Big Boys
Ask any market expert out there what makes the big firms on Wall Street so much more successful than the little guys, and they’ll tell you three things:
- The big boys have more money to hedge with.
- They have better data.
- They use complicated computer systems to make sense of all that data.
For decades, this has created an “unfair” advantage. The big boys have always had an edge.
But with AI, that’s changing.
Few folks know the full history of how AI came into the secretive world of trading, but most research points back to a project called ZagTrader.
By today’s standards, the project was simple. ZagTrader was built to use historical market data to make predictions about future stock prices. (Now we use systems like this all the time.)
What was unique about the idea – and what had the computer department at Carnegie Mellon, where ZagTrader was created, so excited about it – was that the machine could learn from its mistakes.
That’s a trait that most humans think they have… but don’t. We think we learn from our losing trades. But often our logic is off.
We mistake correlation for causation.
Computers are good at figuring these things out. Humans… not so much.
Because of its ability to learn, ZagTrader worked.
It beat the market.
Breakout
Now Wall Street’s biggest firms look to hire folks who have Carnegie’s Tepper School of Business listed atop their gilded degrees. Graduates of the school’s computational finance program have a job offer rate of 98%. Their average salary is $125,000, and signing bonuses stretch as high as $150,000.
Where are they going?
The list of firms includes all the usual suspects – JPMorgan Chase, Citi, Goldman Sachs, Bank of America and BlackRock.
Again… the big boys have been using AI for decades. It shows. That’s why they’re big.
But now, as you may have heard, their competitive edge is waning.
It would be a gross understatement to say that AI has had a bit of a breakout at the retail level recently. It’s the hottest investing trend on the planet. And the trend is only going to get hotter – and more profitable – from here.
Right now, there are many ways for the average investor to take advantage of AI. Some do the work for you… while others you have to put in a bit of work to use.
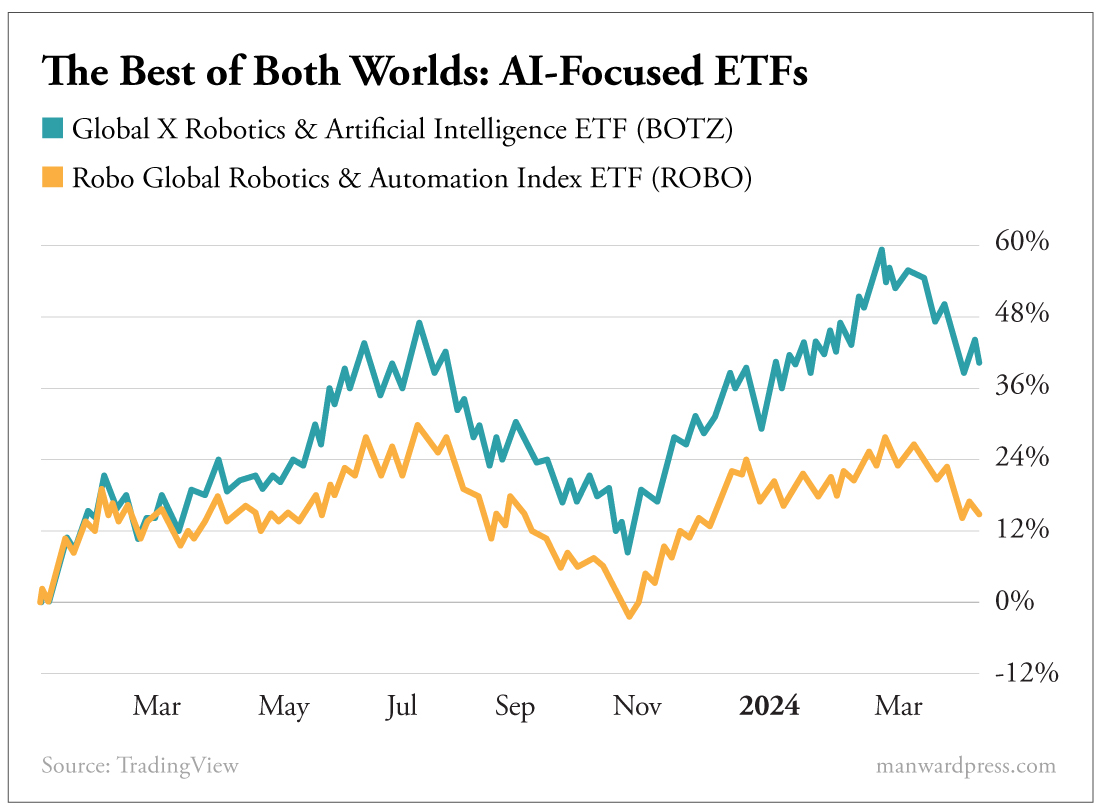
For example, did you know that you have access to AI-focused ETFs – a combination of two of the great financial equalizers of our time?
The Global X Robotics & Artificial Intelligence ETF (BOTZ) has $2.02 billion under its thumb. It invests in companies that use or create AI.
The Robo Global Robotics & Automation Index ETF (ROBO) has $ 927 million in assets.
Each has made a significant leap since the start of 2023.
Best of all, there’s no need to hire expensive computer geeks or shell out for customized programs. Both ETFs have an expense ratio under 1%.
They’re worth considering for the bare minimum amount of exposure to this megatrend.
The newest iterations of AI will create countless jobs… push business productivity and efficiency to new levels… cut costs… boost profits… eliminate diseases…
And deliver windfall profits to businesses… and early investors.
Adding an AI edge to your portfolio is a no-brainer.
Beyond ChatGPT: Understanding How Businesses – and Individuals – Are Harnessing AI Right Now (And Where We’re Heading)
Note From Shah: Early in my career, I bought the first commercially available “brick” cellphone – the Motorola DynaTAC 8000X. It had minute-by-minute cell tower access and talk-time charges. The phone debuted in 1984… and weighed 2.5 pounds. Just 10% of consumers took to that beast or others like it… but 25 years later, 96% of the world owned a cellphone.
Personal computers debuted in the 1980s, but it wasn’t until 2016 that 89% of the world owned one.
And the internet went public in 1993, but it took 23 years for it to reach an 88% adoption rate.
AI’s proliferation will far outpace that of all those other technologies. To say AI’s adoption rate will be unprecedented would be like calling the Grand Canyon a ditch.
AI is already everywhere – and it has been for a while.
Most people just didn’t realize how widespread AI was until ChatGPT came on the scene.
OpenAI’s ChatGPT (GPT stands for “generative pre-trained transformers,” a type of neural network) blew folks away when it launched back in November 2022.
It saw 1 million downloads in its first five days after going public.
Two months later… the novel, easy-to-use AI tool had 100 million monthly users.
And one year after its debut, ChatGPT had 100 million weekly active users… and more than 180 million monthly active users.
That’s just one AI product… one large language model (LLM) trained on massive datasets that enable deep learning algorithms to recognize, translate, predict, and generate text and other content.
According to IBM, a pioneer in the field (remember Garry Kasparov’s chess match with Deep Blue in 1997?), there are three kinds of AI, differentiated by their actual and potential capabilities.
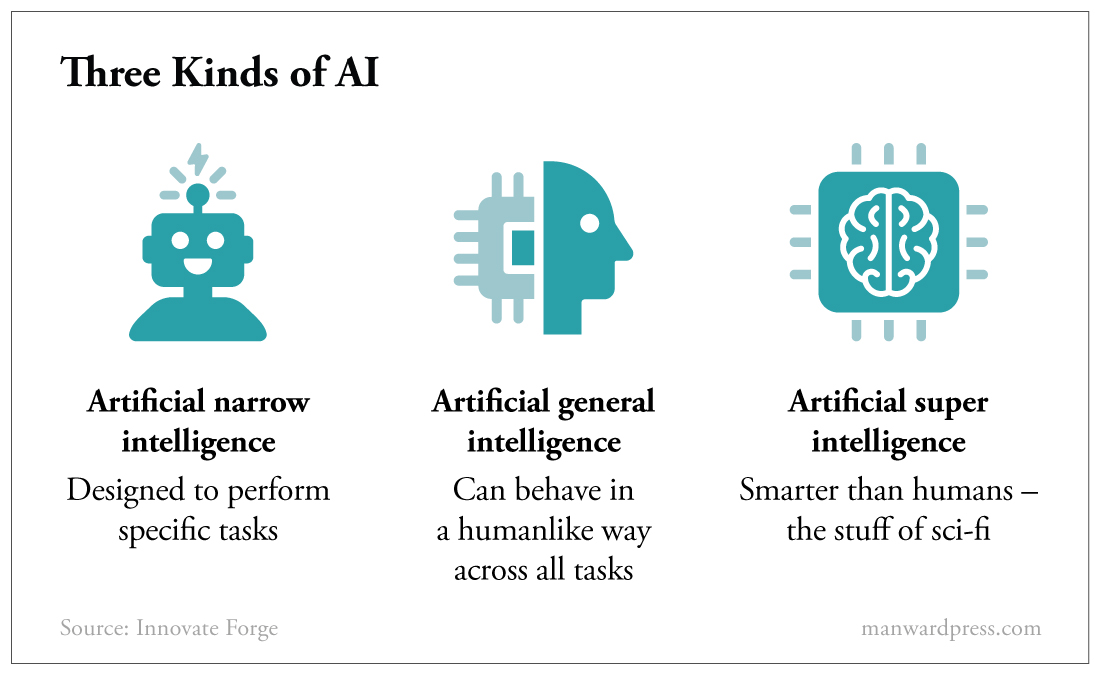
Artificial narrow intelligence, sometimes referred to as weak AI, is the only type of AI that exists today. A weak AI model can be trained to perform a single – or narrow – task, often far faster and better than a human can be.
This type of AI has several subcategories… but the two we are all familiar with are reactive AI and limited memory AI.
Reactive AI systems – think IBM’s Watson or Netflix’s recommendation engine – have no memory. They are built to perform specific tasks. Their output is based on statistics and data.
Generative AI tools, which include LLMs like ChatGPT, Bard and DeepAI… virtual assistant chatbots like watsonx Assistant, Siri, Alexa and Cortana… and even the systems behind self-driving cars… are all limited memory AI programs.
Limited memory AI programs can recall past events and outcomes and monitor specific objects and situations over time. Yet while limited memory AI programs can use past data for a specific amount of time, they can’t retain that data over a long period of time.
Artificial general intelligence, or strong AI, exists today only as an idea. When a strong AI program actually gets developed, it will be able to apply the knowledge it gains to accomplish new tasks in a different context without needing humans to train the underlying models.
And lastly, there’s artificial super intelligence, or super AI. Per IBM, “If ever realized, super AI would think, reason, learn, make judgements and possess cognitive abilities that surpass those of human beings.”
What makes most folks worry about AI is what IBM says next…
Applications possessing super AI capabilities will have evolved beyond the point of understanding human sentiments and experiences to feel emotions, have needs, and possess beliefs and desires of their own.
Meaning… we’re in trouble if the machines learn to think for themselves.
Full Speed Ahead
We don’t say this to create worry. (You know our thoughts on the overblown fears surrounding new technology.) The point is to emphasize just how much more there is to come from AI.
We’re really in the first inning of this ballgame.
For both personal and business uses, AI tools have quickly gone from “fun to play with” to “full speed ahead.”
In a recent McKinsey survey of global executives, one-fourth of respondents said they use AI tools for work. Almost one-third said AI was a priority on their boards’ agendas. Forty percent said their companies had plans to increase their investments in AI this year.
Companies, executives and employees use AI – mostly ChatGPT – to craft first drafts, to summarize texts, to design personalized marketing programs and to identify trends in customer needs.
Chatbots have taken over customer service. Many companies use ChatGPT to help them respond to customer emails.
AI models can forecast trends and anomalies, draft highly technical documents, write code, and create new products.
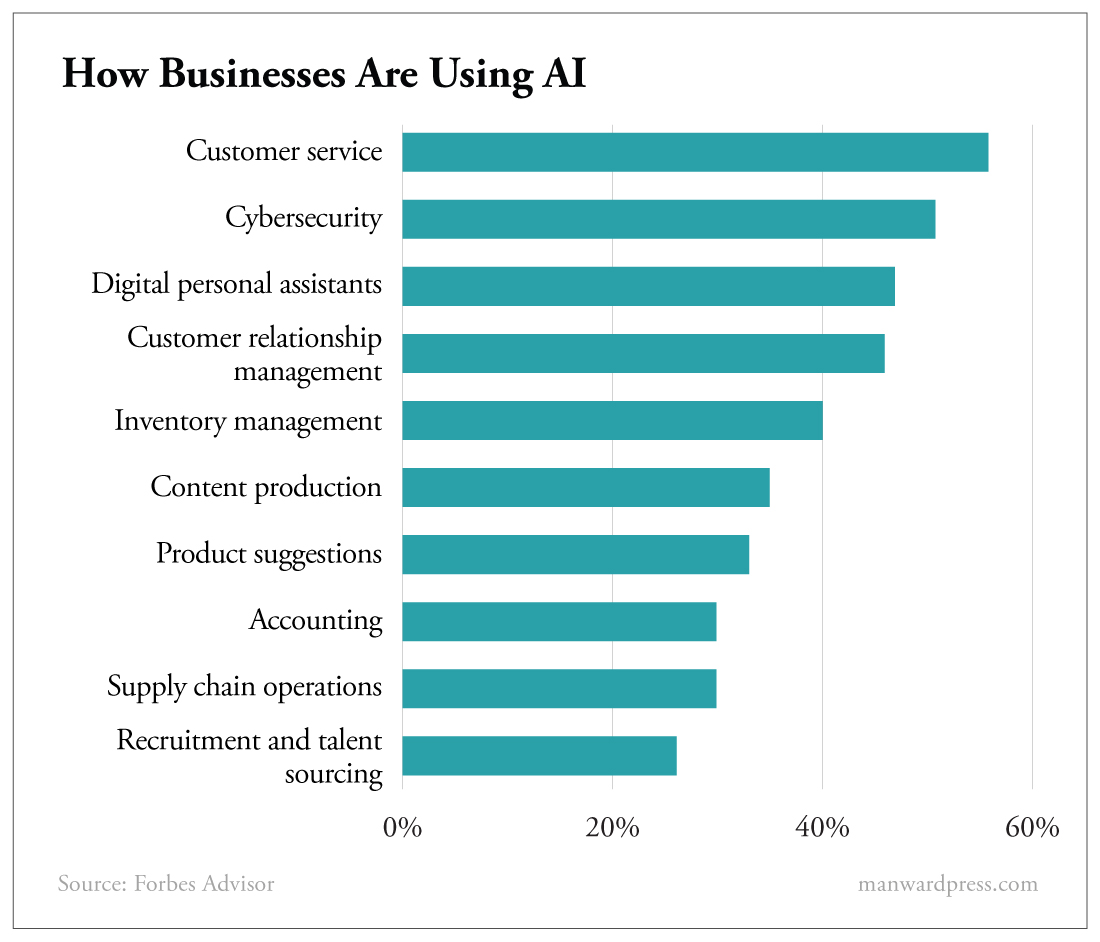
Companies have pretty much been forced to incorporate AI tools into their operations. They know full well that if they don’t, they’ll be left behind.
It’s part of what makes it so difficult to predict just how huge AI expenditures will get. The potential is virtually unfathomable.
It’s the No. 1 thing driving AI stocks higher.
Three-quarters of executives in that McKinsey survey expect there to be “significant disruption” in their fields as AI adoption explodes.
Deloitte’s latest “State of AI in the Enterprise” report revealed that 94% of business leaders believe AI will be critical to their success over the next five years.
With ChatGPT driving consumer adoption, the generative AI market could double every other year over the next decade.
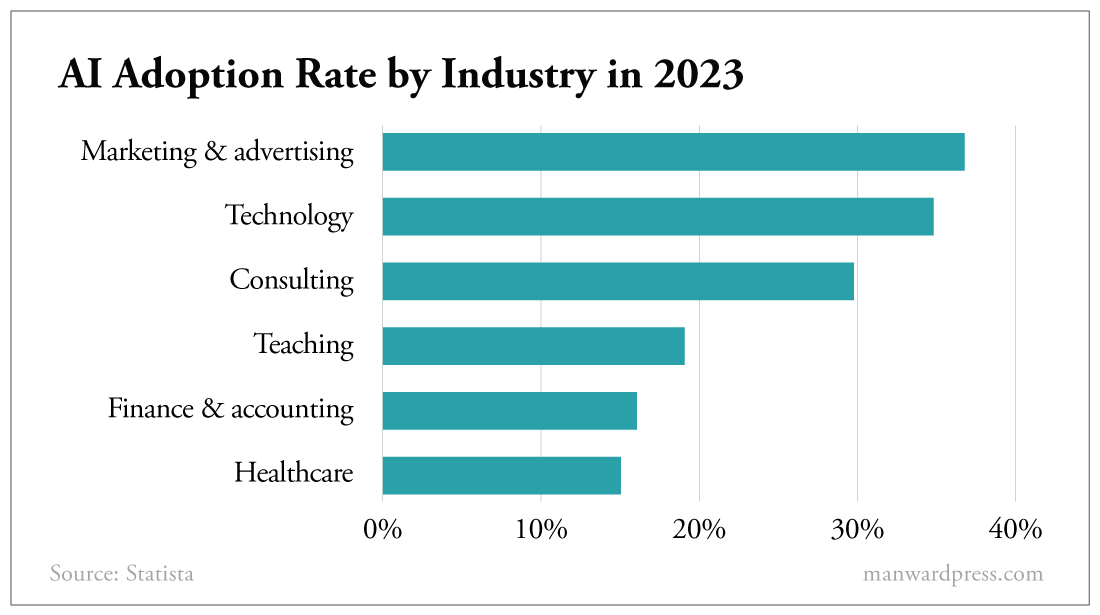
There’s no question AI will transform businesses and create value in many ways…
We’re talking about lower costs, increased efficiency, new growth opportunities, accelerated product and service innovations, and new discoveries and insights relating to business practices.
Corporate executives and managers are increasingly touting AI applications and AI investments in their quarterly earnings reports… in press releases… and through general marketing channels.
Whether they’re actually using AI or are just spinning the narratives investors want to hear is a question worth asking.
According to PricewaterhouseCoopers, 73% of U.S. companies have already adopted AI in at least some areas of their businesses. And globally, more and more companies are touting use cases where AI would enhance products, processes, profits and stock prices.
Here’s the thing…
We’re talking about just one sliver of AI’s capabilities. Improving a business’s bottom line is great for shareholders… but there are some truly astonishing AI developments happening across many sectors… especially healthcare.
It’s an area we’ll explore in the following chapter.
When it comes to AI, almost everything in the business world is at stake. Investors are going to have their work cut out for them separating the pretenders from the legitimate, paradigm-changing juggernauts.
That’s okay. That’s what you have Manward for.
Diagnosis: Profits! The Sector Most Ripe for AI Innovation
Imagine a future where algorithms diagnose diseases with a precision that surpasses what the greatest collaboration of human minds could achieve…
Where the mysteries of diagnosis, prognosis and patient care are solved in the span of a few years… months… or maybe even days.
Already, in our brave – and sometimes scary – new world, the miracles of AI aren’t just knocking on our doors. They’ve barged into our living rooms and lives.
And one sector stands on the brink of a true revolution… an AI revolution we’ve barely begun to comprehend.
Fortunately for all of us, that sector is healthcare.
The application of AI promises a seismic shift in healthcare. From diagnosis and treatment to patient engagement and adherence, AI is revolutionizing every corner of the sector.
It promises a future where precision medicine is the norm, not the exception.
The biggest selling point for AI is that it can analyze vast amounts of data at a speed and depth beyond human capability. That means it can help with early cancer detection, optimize treatment plans and personalize patient care by processing complex datasets, including imaging scans, genetic information and electronic health records.
AI can also improve diagnostic accuracy, reduce false positives in screenings and predict patient outcomes.
Look at This
AI systems are already outperforming radiologists at spotting and differentiating between benign and malignant tumors.
They’re already in widespread use helping clinical researchers decide how to size and construct patient cohorts for hugely expensive and important clinical trials.
A study published by Nature describes the development of algorithms to improve breast cancer detection on mammograms. The AI achieved a high degree of accuracy in sorting images into categories, such as background, malignant mass, benign mass, malignant calcification and benign calcification.
Other studies (reported in the journal Breast Cancer Research) described how AI was used to analyze breast cancer tumors in different types of MRI images. The algorithms demonstrated high detection rates and sensitivity.
Research published in Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology discussed an AI system, trained on mammograms from approximately 91,000 women, which outperformed radiologists in detecting biopsy-confirmed breast cancers in both U.K. and U.S. test sets. The AI demonstrated significant reductions in false-positive and false-negative detection rates. The results suggest AI could play a big role in accurate breast cancer diagnosis.
These examples underscore the significant strides AI and deep learning algorithms have made in the medical field… particularly in the diagnosis of cancer.
They show the ability of algorithms to outperform humans… and highlight the potential they have to revolutionize patient care and clinical research. And there are many companies putting their hats in the ring…
Google-funded startup Enlitic and a host of other private companies are developing AI-derived image interpretation algorithms.
Enlitic, for example, is using deep learning for tumor detection. The company has designed algorithms that detect lung tumors through CT scans.
That’s a huge advancement in diagnosing critical diseases at an early stage.
Jvion, recently bought by Lightbeam Health Solutions, offers a “Cognitive Clinical Success Machine.” It identifies patients most at risk as well as those most likely to respond to treatment protocols.
Companies like these are already providing support to clinicians in finding the best diagnoses and treatments for patients.
And others are tackling another huge, costly problem in healthcare… Paperwork.
Paper Pushers
The healthcare sector is trapped in a nonstop digital tsunami of medical data. I’m talking about patient profiles, research papers, procedures and surgeries, drug development trials and treatments, genomic studies, you name it… It all floods the healthcare system.
AI offers new ways to deal with the complexities of patient care, treatment protocols, drug discovery and preventive care.
Here are just a few of the ways AI is helping to relieve the burden of medical paperwork…
- Medical transcription: AI-powered software can transcribe medical notes and reports from voice recordings, saving time for healthcare professionals and reducing errors.
- Data entry and extraction: AI can automatically extract relevant information from medical documents, such as patient records, test results and insurance forms, and enter it into electronic health record systems.
- Claims processing: AI can help automate the processing of insurance claims by verifying patient eligibility, checking for errors and ensuring compliance with regulations.
- Coding and billing: AI algorithms can assist with medical coding and billing by suggesting appropriate codes for diagnoses and procedures, reducing errors and improving accuracy.
- Prior authorization: AI can help streamline the prior authorization process by automatically checking patient information against insurance requirements and submitting necessary documentation.
- Document classification: AI can categorize and organize medical documents, making it easier for healthcare professionals to find and access relevant information.
- Fraud detection: AI algorithms can analyze medical claims and billing patterns to identify potential fraud or abuse, helping to reduce healthcare costs and improve the efficiency of the system.
And it’s all being made possible by companies big and small…
Amazon (AMZN) has introduced HealthScribe, an AI tool that helps summarize doctor visits. Alphabet is testing a medical chatbot in hospitals.
An AI platform from the company Abridge can automatically document clinicians’ interactions with patients.
HCA Healthcare (HCA) is collaborating with Google Cloud on the use of generative AI to support doctors and nurses by reducing the burden of administrative tasks. One solution extracts information from physician-patient conversations to help create medical notes.
Another aims to make the nurse handoff easier. Nurses communicate things like a patient’s vitals, lab results, concerns and overall response to treatment to help the incoming nurse get up to speed. AI can standardize and automate this process, helping promote continuity, consistency, patient safety and clinical quality… and save time.
By automating repetitive tasks and reducing the administrative burden on healthcare professionals, AI is helping to improve the efficiency and accuracy of medical paperwork. And that will ultimately lead to better patient care and outcomes.
But Wait… There’s More
The impact of AI on drug discovery will be just as profound. AI-designed drug molecules are entering human clinical trials. AI systems like AlphaFold predict protein structures.
These advancements not only expedite the drug discovery process but also promise to usher in a new era of healthcare treatments by significantly reducing both the time and the costs associated with drug development.
In the operating room, AI-driven surgical robots and preoperative planning tools are aiding in minimally invasive surgeries, improving surgical outcomes and reducing healthcare costs.
AI assists in tissue tracking during surgery and has been instrumental in robotic hair restoration and cardiac surgery performed with minimal incisions.
Now, some folks may be skeptics… and have concerns about AI taking over the most personal and intimate details of their lives. But as we’ve seen in examples throughout time, AI is unlikely to replace human clinicians or healthcare providers.
Instead, it will augment their capabilities… and it will free them from the drudgery of administrative tasks and empower them to focus on what they do best… Caring for patients.
The role of the clinician will evolve, drawing more on uniquely human skills, like empathy, persuasion and big-picture thinking.
Most AI evangelists see a world in which AI and human ingenuity converge, creating healthcare systems that are more accessible, accurate and attuned to the needs of patients.
The battle against disease will be waged not just in laboratories and clinics but within the vast neural networks of AI, offering hope where once there was none.
How to Start Using AI Now… and Gain Some Valuable Know-How in the Process
Publisher’s Note: At this point, we’ve been covering AI for more than five years. Back in 2018, we were among the first to make note of Apple’s (then) newly launched AI research facility. Half a decade later, the opportunities in the AI sphere continue to grow. It’s clear that AI is already helping us do important things. But the question is… Have you dipped your toes in yet?
Yes, we are talking to YOU, dear reader.
If you’ve been with us since our early days, you understand the value of hard-earned Know-How. It’s one of the core values that defined Manward’s path when we launched.
If we stop learning… we stop living. Or, as Henry Ford once put it…
“Anyone who stops learning is old, whether at 20 or 80. Anyone who keeps learning stays young.”
And so, as we once did with our popular “Old Guy’s Guide to Crypto” series, we’re going to help you add a new and powerful tool to your tool kit.
To do that, we’ve assembled a quick primer on the biggest name in the AI game today… ChatGPT.
If you’re interested in what you’ve seen so far (we sure hope that’s the case) and want to try using AI for yourself, keep reading.
As with any new skill, the best way to learn is to simply… do.
And one of the great things about AI is…
Despite the sky-high valuations… soaring stock prices… and GDP-altering potential…
Anyone can tap into AI – right now – without spending a dime.
To get your feet wet with ChatGPT, you just need to create a free account…
How to Get Started
Start by going to chat.openai.com.
Click “Sign up” to get started. You’ll be prompted to begin the registration process from scratch. Or you can link a Google, Apple or Microsoft account.
It couldn’t be simpler. (No wonder ChatGPT was able to garner 100 million users in less than a year.)
Once this quick process is complete, you’ll be greeted by a few disclaimers. They essentially state that the software is still a work in progress and may generate incorrect responses to certain queries. You’ll also get a note stating that whatever you put into the chat may be reviewed by OpenAI’s staff to help improve ChatGPT.
So don’t go putting in any sensitive details (this is still the internet, after all).
With all of that squared away, you’ll be off to the races. Your screen should look something like this…
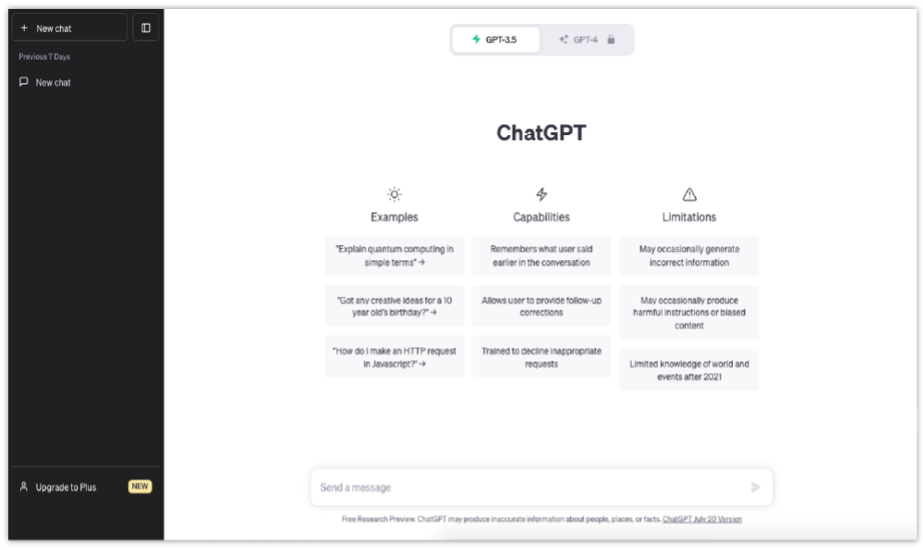
See that text bar at the bottom of the screen? That’s where you’ll put in your first prompt.
This is where things get fun.
Sample Prompts
You might be wondering what sorts of things you can ask ChatGPT. That’s kind of the beauty of the system… You can pretty much ask it anything.
Depending on your personality, that may excite you… or unnerve you. Either way, allow us to provide an example of some good opening questions.
Since we are, at our core, a financial publisher, let’s start with a simple question we’ve gotten from folks just getting started as traders…
“Can you explain how stock options work to me like I’m a 10-year-old?”
When we asked this, ChatGPT replied…
Alright, imagine you have a really cool trading card of your favorite superhero, let’s call it “Super Option.” Now, you know that other kids might want to have this card too because it’s so awesome. So, you decide to let them borrow it for a little while.
Now, here’s the fun part: You tell them, “Hey, you can borrow this card for two weeks, and if you still want it after that time, you can buy it from me for $5.” The other kids think it’s a great deal because they might not be sure if they really want the card, but they get to try it out for a while.
Now, let’s translate this to the stock market! Instead of trading cards, we have stocks of real companies like “SuperTech Inc.” When you buy a stock, you own a tiny piece of that company. But sometimes, you’re not sure if the stock price will go up or down.
That’s where stock options come in…
The software then went on to explain the difference between call options and put options in a way that might truly make sense to a 10-year-old (or someone just learning about investing). It even included a handy disclaimer about the risks of trading options.
Here’s another example…
“What should I look for in a good value stock?”
ChatGPT gave a lengthy response that started with…
Looking for a value stock involves identifying companies whose stock prices appear to be undervalued compared to their intrinsic value. Here are some key factors to consider when looking for a value stock…
It then listed 10 criteria value investors should consider, including a low P/E, a solid dividend yield, consistent free cash flow and more.
And, yes, it provided another disclaimer.
One more…
“How do cryptocurrencies work?”
ChatGPT explains…
Cryptocurrencies work on the principles of blockchain technology, a decentralized and distributed ledger system. Let’s break down the key components of how cryptocurrencies work…
The software went on to tell us – in simple terms – how blockchains record crypto transactions, how transaction validation occurs, what Proof of Work and Proof of Stake mean, and more.
It also warned of the dangers of trading cryptocurrencies without a proper understanding of the risks involved. (Hear! Hear!)
In our humble opinion, while this response may not be quite as well written or useful as Manward’s official crypto guide, it’s far from shabby.
We dare say it’s even good.
The point is… ChatGPT can provide simple and sometimes in-depth answers to prompts like our examples above. Just be aware that this software is still learning and growing – and is prone to occasional mistakes.
What It All Comes Down To
Naturally, in our sample prompts, we kept things basic and focused on the financial realm. But we invite the curious to simply log in to ChatGPT and take it for a spin.
Think of it as an ultrasmart, souped-up search engine. Ask it whatever pops into your mind (assuming what pops into your mind isn’t your Social Security number or your mother’s maiden name). As it stands, there’s no wrong way to use ChatGPT.
If nothing else, you’ll get a firsthand peek at what all the AI hype is about… even if ChatGPT itself represents only a tiny sliver of what this new technology promises.
Try it out… and gain some valuable Know-How in the process.
Sample Prompts to Analyze Any Stock
While ChatGPT and other major AI services aren’t explicitly built as trading tools, they can help you conduct surface-level analysis of any stock. Here are some samples of our favorite prompts we’ve used so far…
- “Summarize the key points from [Stock]’s latest earnings report.”
- “Analyze the current market sentiment surrounding [Stock].”
- “Compare the trading volume of [Stock X], [Stock Y] and [Stock Z] over the past quarter.”
- “Look at the six-month price history of [Stock] and identify any patterns.”
- “Analyze the potential impact of Federal Reserve announcements on [Stock] stock price.”
Focusing on AI stocks and the broader tech market, you might say…
- “Compare the intraday price movements of [AI Stock X] and [AI Stock Y] over the past month.”
- “Calculate the price-to-earnings ratio of [AI Stock] and compare it to the AI sector as a whole.”
- “Analyze the key differences between [AI Stock X] and [AI Stock Y].”
Give these a try and use them as starting points to create your own prompts. Just remember to do your own due diligence before taking any market action.
ChatGPT is a great tool. But it is NOT a financial advisor.
In Sum: AI Terminology and FAQs
We’ll end with a roundup of the key terms and FAQs surrounding AI.
You can consider the following a summary of all we’ve explored in our AI Handbook… and an appendix you can reference as you continue to learn about this booming sector.
But why don’t we wrap things up by asking AI to speak for itself…
Why should we explore investment opportunities in AI?
Here’s what ChatGPT had to say…
- AI stands as a colossal and burgeoning market. Industry projections from Markets and Markets anticipate the global AI market size will reach an estimated $1.34 trillion by 2030, expanding at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 36.8% from 2023 to 2030. AI applications span across almost every sector of the market, including healthcare, education, finance, retail, manufacturing, entertainment and more. As AI technology becomes more accessible, cost-effective and scalable, the demand for AI solutions is expected to surge dramatically.
- AI serves as a source for competitive advantage and innovation. Businesses harness AI to enhance efficiency, productivity, quality, customer satisfaction and profitability. Additionally, AI empowers companies to craft new products and services, enter untapped markets, and gain a competitive edge over their industry counterparts. For instance, Adobe (ADBE) leverages AI and machine learning (ML) to augment its creative software suite, providing personalized experiences for its customers. Alphabet (GOOGL), the parent company of Google, integrates AI into its search engine, digital assistant, cloud computing and self-driving cars. Nvidia (NVDA) excels in developing graphics processing units (GPUs) and chips that fuel AI applications in gaming, data centers, automotive and healthcare.
- AI promises to be a long-term driver of growth. Despite being in its infant stages of development and adoption, AI technology offers immense potential for improvement and innovation in both its technology and applications. As AI advances in sophistication, intelligence and ubiquity, it will unlock new value and opportunities for businesses and society. Investing in AI stocks at present could grant exposure to the future leaders and beneficiaries of this technological revolution.
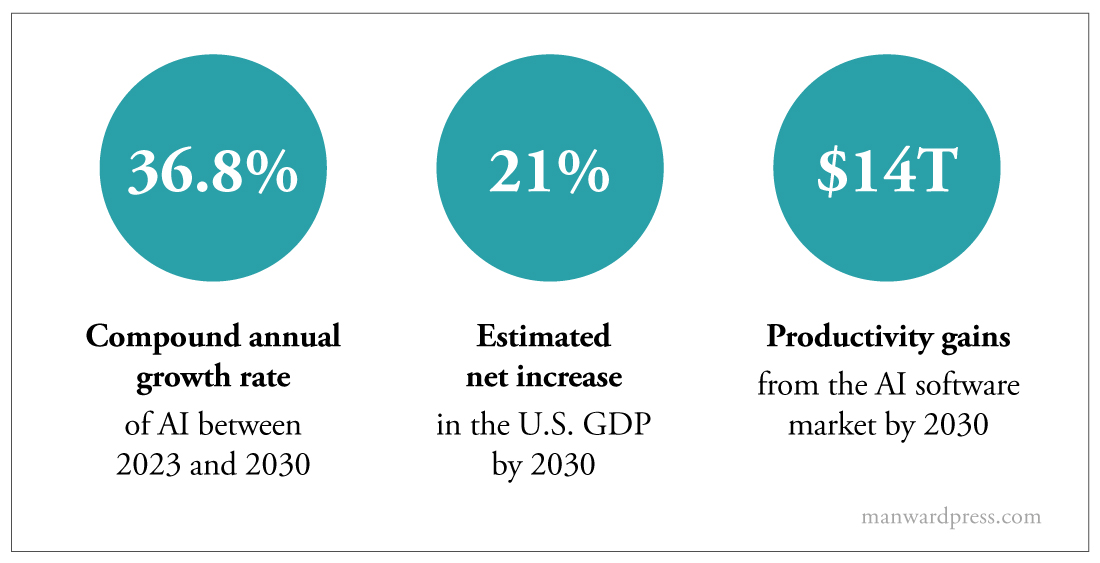
Now on to that key AI terminology, starting with the basic definition of AI itself…
- Artificial intelligence (AI)
At its core, AI refers to the development of computer systems capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. These tasks include learning, problem solving, decision making and language understanding. AI encompasses various subfields, including machine learning and natural language processing. - Machine learning (ML)
Machine learning is a subset of AI that enables systems to learn and improve from experience without explicit programming. ML algorithms use data to identify patterns, make predictions and adapt to new information, powering applications like recommendation systems, fraud detection and autonomous vehicles. - Natural language processing (NLP)
NLP focuses on enabling machines to understand, interpret and generate human language. It involves tasks such as language translation, sentiment analysis and speech recognition. NLP forms the basis of virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa and Google Assistant. - Deep learning
Deep learning is a specialized form of machine learning that utilizes artificial neural networks to simulate human decision making. These networks, inspired by the human brain, can recognize patterns in unstructured data such as images, audio and text. Deep learning powers advancements in image recognition, speech synthesis and self-driving cars. - Neural networks
Neural networks are a key component of AI, mimicking the human brain’s structure to process and analyze complex data. Comprising interconnected layers of artificial neurons, these networks learn patterns and relationships in data, making them a fundamental aspect of ML and deep learning. - Big data
Big data refers to the massive volume of structured and unstructured data generated daily. AI systems rely on this data to learn, analyze and make predictions. The insights extracted from big data play a crucial role in improving AI models and applications. - Algorithm
In AI, an algorithm is a set of rules or instructions that enables a computer to solve a problem or perform a task. AI algorithms process data, make decisions and continuously improve based on feedback and new information. - Robotics
Robotics is a vital domain within AI that involves the design and development of robots. These machines can operate autonomously or under human guidance to perform tasks ranging from assembly line work in manufacturing to complex surgeries in healthcare. - Computer vision
Computer vision, a specialized subset of AI, focuses on teaching computers to interpret and analyze images and videos. It enables machines to recognize objects, understand scenes and extract valuable information from visual data. - Reinforcement learning
Reinforcement learning is a specific type of machine learning. It revolves around training agents to take actions in an environment, learning through trial and error to maximize a reward signal. It’s widely used in creating autonomous systems and game-playing algorithms. - Natural language generation (NLG)
NLG, an offshoot of natural language processing (NLP), involves instructing machines to generate human-like language. This technology powers chatbots, automated content creation and summary generation. - Expert systems
Expert systems are AI systems designed to replicate the decision-making capabilities of a human expert in a specific domain. These systems leverage knowledge and rules to provide guidance or solutions to problems. - Data mining
Data mining involves the exploration and analysis of large datasets using statistical and computational methods to reveal patterns, correlations and valuable insights. AI systems often rely on this process to improve their learning and predictive abilities. - Artificial intelligence ethics
AI ethics is the study of the ethical, social and political implications of AI systems and their applications. It examines issues such as bias in algorithms, privacy concerns and the impact of AI on society. - Explainable AI
Explainable AI refers to AI systems and models capable of providing explanations or justifications for their decisions or predictions. This feature is crucial in ensuring transparency and trust in AI applications. - Generative adversarial networks (GANs)
A GAN is a sophisticated form of deep-learning model involving two neural networks. One network generates synthetic data, while the other discerns between authentic and fabricated data. GANs have found applications in creating synthetic images, videos and text. - Convolutional neural networks (CNNs)
CNNs are a specific type of neural network frequently employed in tasks like image recognition and computer vision. They are adept at processing visual data due to their ability to recognize patterns in images. - Hallucinations
Hallucinations in the context of AI refer to instances in which large language models generate text that seems coherent and meaningful but lacks grounding in factual information or reality.
FAQs: Understanding the AI Industry
As you now know, the AI industry is made up of a wide variety of segments, applications and stakeholders all engaged in developing, implementing and utilizing AI technologies.
These powerful systems are capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, decision making and creativity.
What Are the Main Segments Within the AI Industry?
- Machine learning: Enabling machines to learn from data and enhance their performance without explicit programming, it encompasses subfields such as supervised learning, unsupervised learning, reinforcement learning, deep learning, generative models and natural language processing.
- Computer vision: Empowering machines to interpret and analyze visual information, performing tasks like face recognition, object detection, scene understanding and augmented reality.
- Speech recognition: Enabling machines to recognize and process human speech and audio signals for tasks like voice assistants, transcription, translation and speech synthesis.
- Robotics: Creating machines that can interact with their environment. These are often used in manufacturing, exploration, entertainment and healthcare.
What Are the Main Applications That Exist Within the AI Industry Today?
- Marketing and sales: Optimizing strategies by analyzing customer behavior and preferences, generating personalized content, and offering targeted recommendations.
- Product and service development: Innovating products and services by incorporating user feedback, market trends and competitive analysis to automate design and testing processes.
- Strategy and corporate finance: Improving strategic and financial decisions by providing insights into market opportunities, risk management and resource allocation.
- Supply chain management: Optimizing supply chain operations by forecasting demand, inventory and delivery while monitoring and enhancing quality and efficiency.
Who Are the Key Players Within the AI Industry?
- AI providers: Develop and offer AI products and services to businesses and consumers. Examples include Google, Microsoft, IBM, Amazon and Meta.
- AI adopters: Utilize AI products and services to improve their business processes or offerings. Examples include Netflix, Spotify, Uber and Airbnb.
- AI enablers: Provide infrastructure or platforms supporting the development or deployment of AI products and services. Examples include Nvidia, Intel, AWS and Azure.
- AI regulators: Establish rules and standards for the ethical and responsible use of AI. Examples include governments, international organizations and industry associations.
For more about AI – including our experts’ favorite ways to invest in the sector right now – explore our latest commentary at ManwardPress.com and TotalWealthResearch.com.
Note: We’ve found that readers tend to buy the stocks in these special reports at different times. Keep in mind that we may have taken profits or stopped out of a recommendation by the time you read this report. Please refer to the current portfolios for the most up-to-date recommendations.
© 2025 Manward Press | All Rights Reserved
Nothing published by Manward Press should be considered personalized investment advice. Although our employees may answer your general customer service questions, they are not licensed under securities laws to address your particular investment situation. No communication by our employees to you should be deemed as personalized investment advice. We allow the editors of our publications to recommend securities that they own themselves. However, our policy prohibits editors from exiting a personal trade while the recommendation to subscribers is open. In no circumstance may an editor sell a security before subscribers have a fair opportunity to exit. The length of time an editor must wait after subscribers have been advised to exit a play depends on the type of publication. All other employees and agents must wait 24 hours after publication before trading on a recommendation.
Any investments recommended by Manward Press should be made only after consulting with your investment advisor and only after reviewing the prospectus or financial statements of the company.
Protected by copyright laws of the United States and international treaties. The information found on this website may only be used pursuant to the membership or subscription agreement and any reproduction, copying or redistribution (electronic or otherwise, including on the world wide web), in whole or in part, is strictly prohibited without the express written permission of Manward Press, 14 West Mount Vernon Place, Baltimore, MD 21201.
April 2025.

